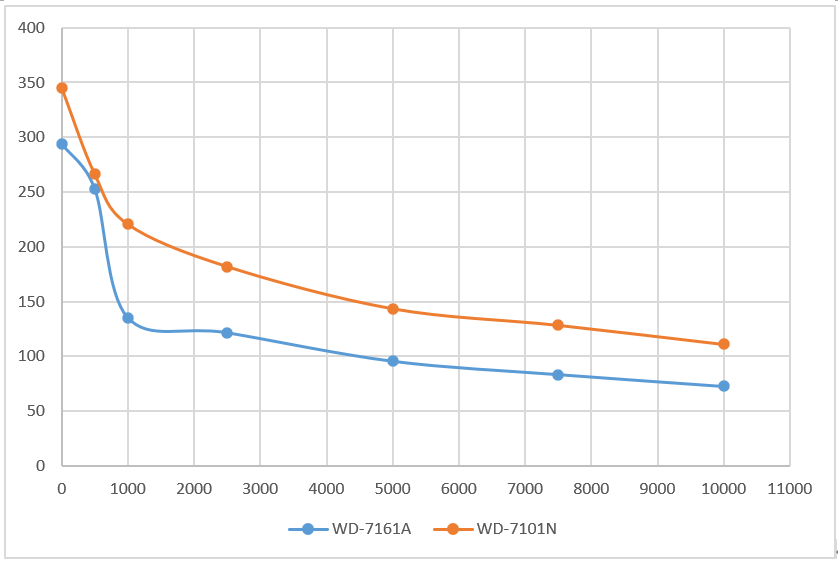
Polyacrylamide has poor salt resistance, shear resistance and certain chemical degradation. Therefore, the salt tolerance and viscosity enhancement of polymer (PAM) oil displacement agent has become a very challenging research topic in EOR technology. Using two kinds of polyacrylamide of our company as raw materials, the viscosity of polyacrylamide aqueous solution with different salinity solvents was studied at room temperature, and the viscosity reducing effect of metal ions on polyacrylamide was studied by measuring the viscosity under different conditions. The experimental results show that the higher the concentration of polymer, the greater the viscosity of polyacrylamide aqueous solution; when the concentration of polymer is constant, the viscosity of aqueous solution decreases with the increase of salt concentration, and the viscosity of the system decreases more obviously. When the amount of salt reaches a certain degree, the viscosity of the system no longer decreases. Among the ions of these salts, the effect of divalent ions such as calcium, magnesium and barium on the viscosity of polyacrylamide aqueous solution is obvious, and the effect on the viscosity of polyacrylamide aqueous solution is Ca2+ > Mg2+ > Ba2+ > K + > Na+. The following figure is sorted out according to the experimental data: from the trend of the curve, we can see that the salt resistance of WD-7101N is better than that of WD-7161A in WD-7161A,1000ppm and slightly stronger than that of WD-7101N.If you want more details, please contact us.