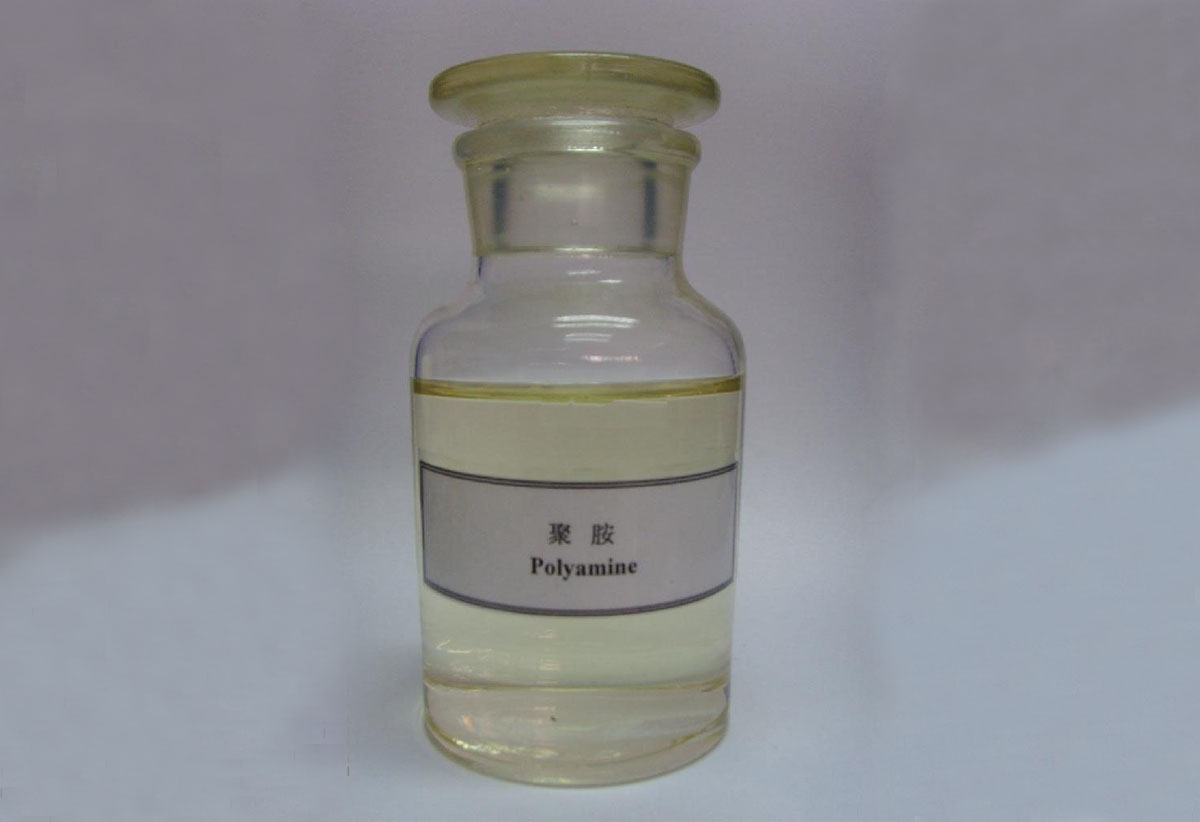
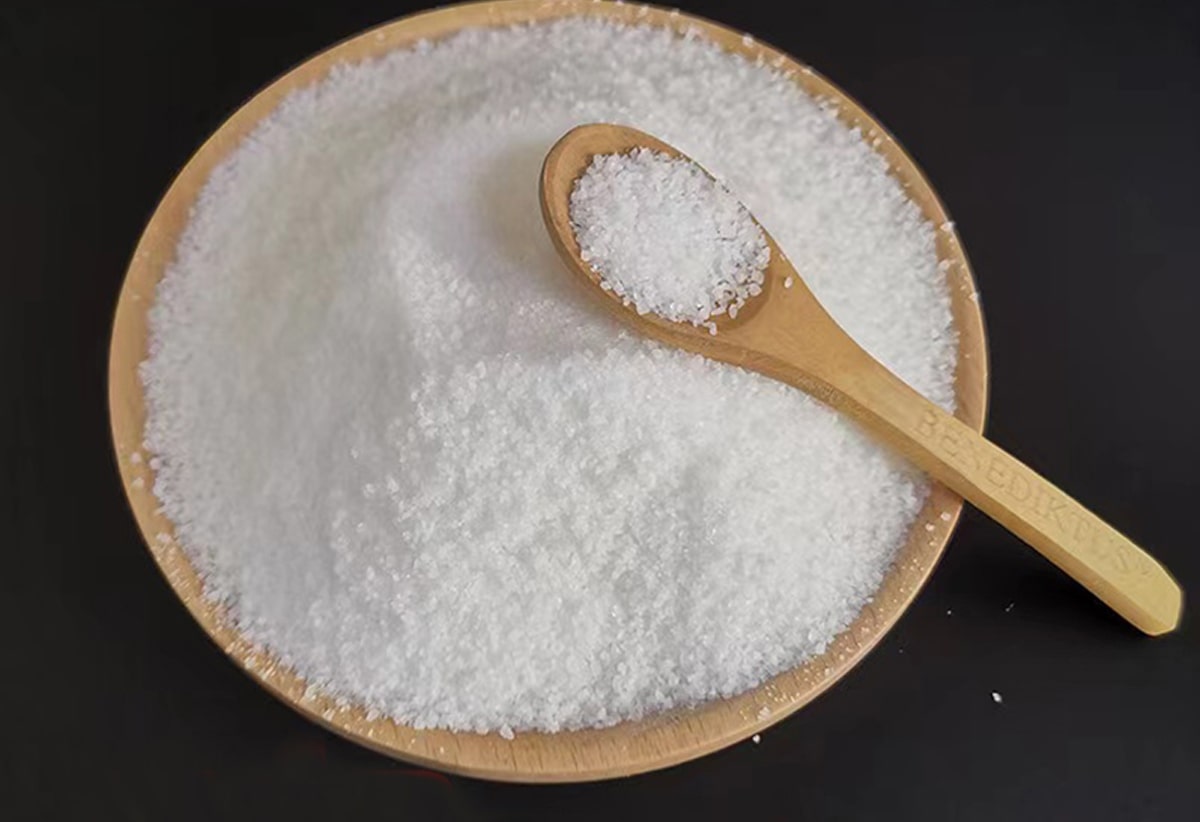
Product form:White powder
molecular weight:3 million -20 million
Degree of hydrolysis:0-50%
Dissolution time:30min-2h
Solid content:>88%
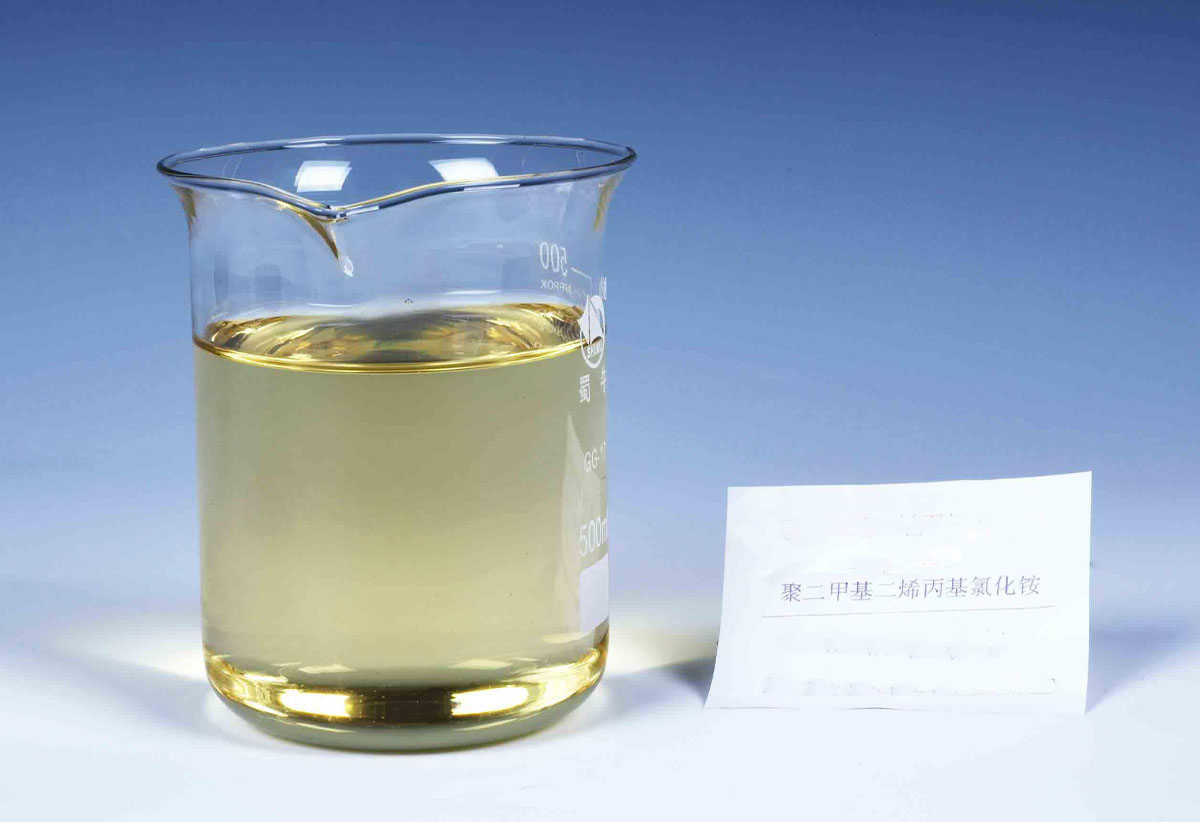
Product form:latex
molecular weight:8 million -20 million
Degree of hydrolysis:0-50%
Dissolution time:20min
Solid content:35%-40%
DRILLING
IMPROVING WELL PERFORMANCE, REDUCING NON-PRODUCTION TIME
WELLDONE supports our customers in delivering optimized drilling and completion programs with maximum efficiency to enable production-ready wellbores. Economic drilling of oil wells requires specific properties for drilling fluids supported by world-class supply chain and logistics. Many demands are placed on these fluids to achieve multiple objectives, such as:
*Enabling cuttings transport
*Maintaining a cool and clean drill bit
*Preventing differential sticking
*Preventing inflow of formation fluids
*Ensuring wellbore stability
*Minimizing fluid loss
WELLDONE produces a range of specifically engineered polymers for water-based drilling fluid systems in powder, liquid, and emulsion forms in various packaging to meet individual needs. Each series of polymers meets one or several requirements, such as fluid-loss control, viscosity improvement, high temperature/high-pressure (HTHP) applications, and shale inhibition. These polymers are produced in a variety of physical forms, molecular weights, and compositions for specific applications. SNF drilling fluid polymer additives include:
*Viscosifiers (emulsion fluid systems and water-based)
*Solids Suspending Agents
*Brine Viscosifiers
*Bentonite Extenders
*Fluid-Loss Control Agents for Mud
*Dewatering Additives
*Thinners/Dispersants
*Rheology Modifiers
*HTHP Applications
*Solids Control
Polyacrylamide is used as an oilfield drilling fluid to improve drilling fluid performance, prevent well wall collapse, cool drill bits and lubricate drill bits, and suppress wall collapse. Polyacrylamide for drilling fluids can be applied to low solid phase non-dispersible polymer drilling fluid systems, can be used in combination with a variety of treatment agents, and is suitable for various mud systems.
Features:
1. Shale inhibitors: inhibit the hydration, expansion and decomposition of clay minerals contained in shale to prevent well collapse
2. Filtration loss: controlling water entering the formation leads to hydration and expansion of mud shale
3. viscosity reduction: concentrated on protecting the edge of clay particles, enhance the negative electrical effect at the place, so that the system can not form a grid structure and thus play a role in reducing viscosity.
| User name | Member Level | Quantity | Specification | Purchase Date |
|---|